Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion.…
Heat transfer is the transfer of heat or thermal energy between physical systems. So when there is a temperature difference between two bodies, heat is transferred from the hot body to the colder body. There are three common modes of heat transfer – conduction, convection, and radiation. In this article,…
Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and polar molecules, such as ions, proteins, and polysaccharides, while being permeable to non-polar or hydrophobic molecules like lipids as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon…
A well-known chemistry experiment is done by placing an egg (raw or boiled) into a container filled with Vinegar. After a few days, something exciting is observed: the egg becomes rubbery and bouncy. The eggshell is formed by calcium carbonate (CaCO3), a salt in limestone, plaster, marble, chalk,…
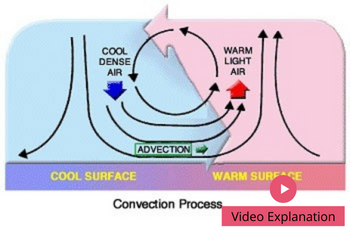
The heater is placed near the floor because the air currents move upwards so the hot air fills up the whole room. Whereas, an air conditioner is placed near the ceiling because the cold breeze tends to settle down. If it is placed near the floor then it will fill just…
The vacuum flask consists of two vessels, one placed within the other and joined at the neck. The gap between the two vessels is partially evacuated of air, creating a partial-vacuum which reduces heat conduction or convection. Heat transfer by thermal radiation may be minimized by silvering flask surfaces…
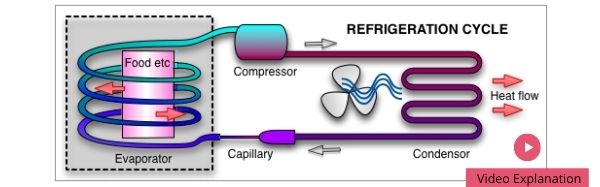
It could simply be that black paint is cheaper… But I believe that the external coils on the back of refrigerators are painted black for the following reason: There is a rule in nature that says “a color that is better at absorbing heat is also better at radiating heat.” …
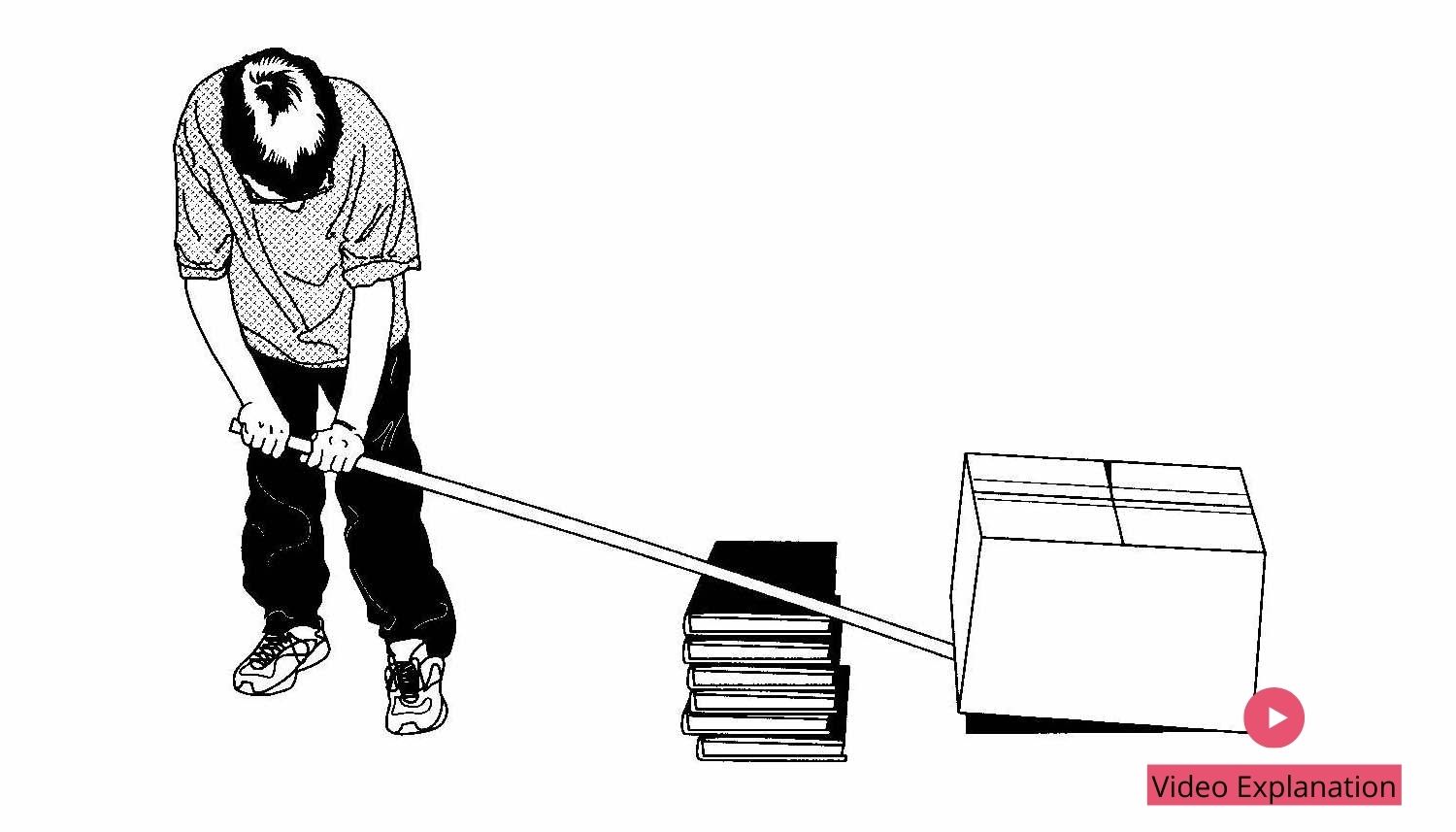
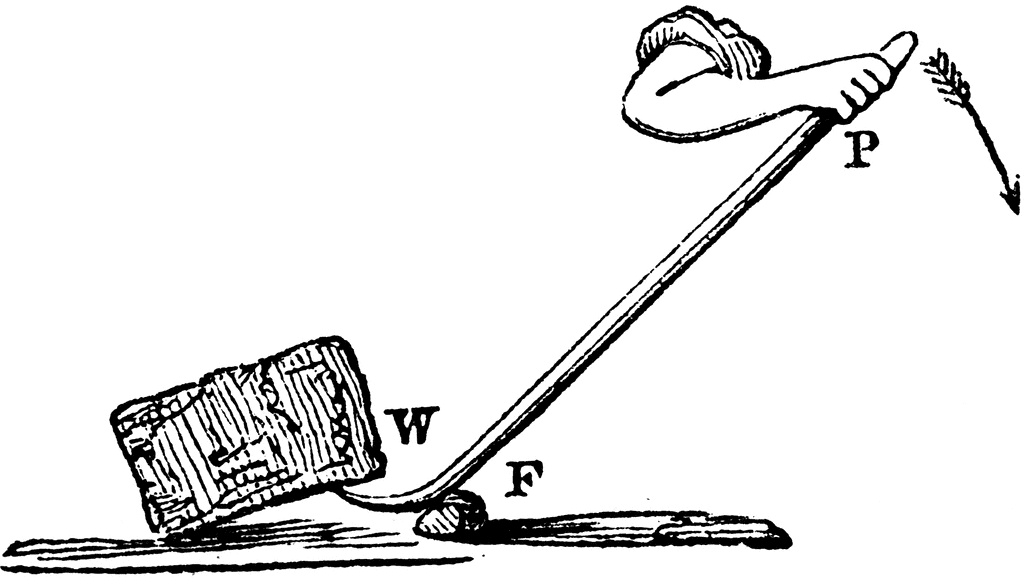
We encounter various types of lever in our everyday lives: opening a drink with a bottle opener, cutting paper with scissors, taking the lid off a paint pot using a screwdriver, and – the simplest of all – playing on a seesaw in the park. Yet, the principle of…
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided…
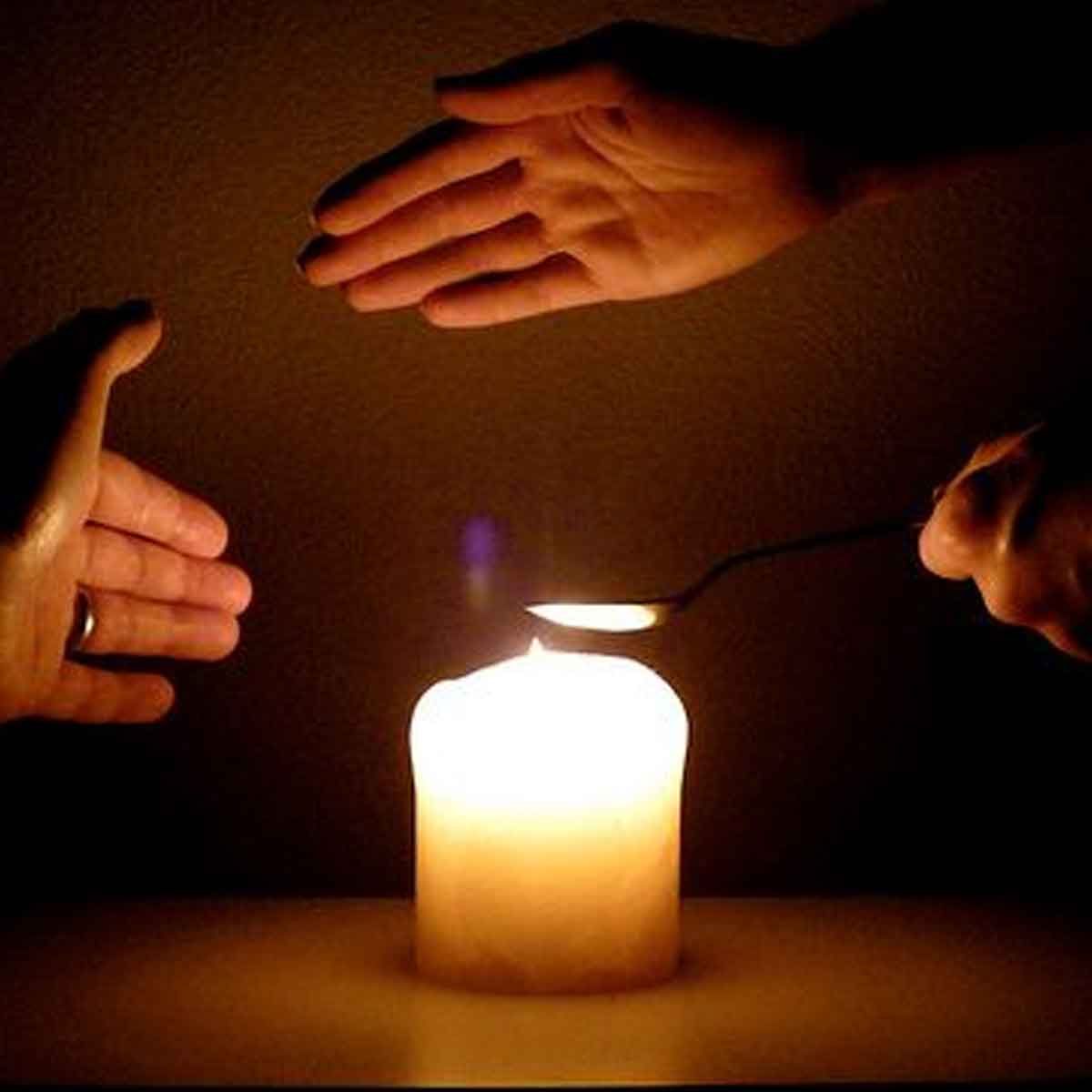
According to heat definition, it is one of the essential forms of energy for the survival of life on earth. Transfer of heat takes place from one body to another due to difference in temperature as per thermodynamics. We use heat energy for various activities like cooking, ironing, transportation,…
Microorganisms A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. 0
A microorganism is a living thing that is too small to be seen with the naked eye. Examples of microorganisms include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, and microscopic animals such as the dust mite. Microorganisms are found virtually everywhere, except for environments that have been made artificially sterile by humans. Even…
Geometry is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space that are related with distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer. 0
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn, form a sequence, the Fibonacci sequence, in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors omit the initial terms and start the sequence from 1 and 1 or…
No single answer to the question “What is light?” satisfies the many contexts in which light is experienced, explored, and exploited. The physicist is interested in the physical properties of light, the artist in an aesthetic appreciation of the visual world. Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation within the…