Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion.…
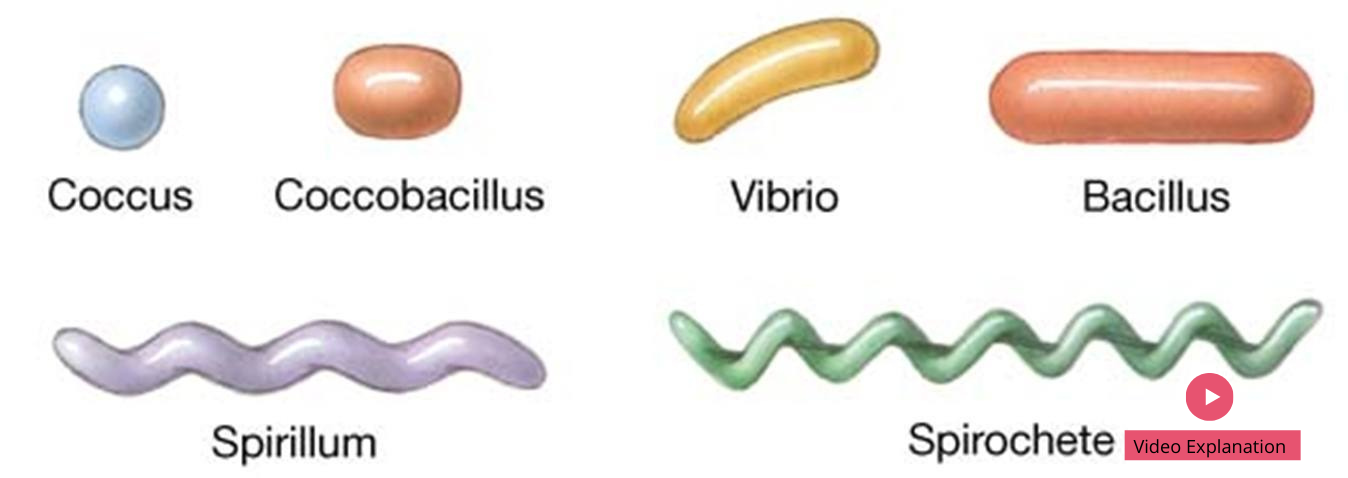
A microorganism is a living organism that is so tiny it can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. Consider that the largest human cells are about the diameter of a human hair. Bacteria cells are one-hundredth the size of a human cell and viruses are much, much smaller again. If you imagine that…
Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and polar molecules, such as ions, proteins, and polysaccharides, while being permeable to non-polar or hydrophobic molecules like lipids as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon…
Microorganisms A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. 0
A microorganism is a living thing that is too small to be seen with the naked eye. Examples of microorganisms include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, and microscopic animals such as the dust mite. Microorganisms are found virtually everywhere, except for environments that have been made artificially sterile by humans. Even…
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Cells can acquire specified function and carry out various tasks within the cell such as replication, DNA repair, protein…
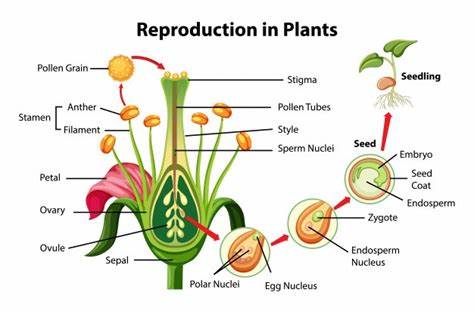
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from either parent. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes. The resulting clonal plants…
Heredity is a process in which organisms acquire characteristics from their parents. These characteristics are called traits. Every individual is unique because they have a unique set of traits. The traits which are transmitted by the parent to its offspring during the process of fertilization are inherited traits. This inheritance…
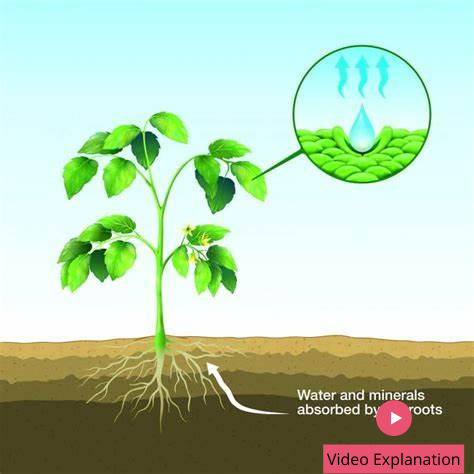
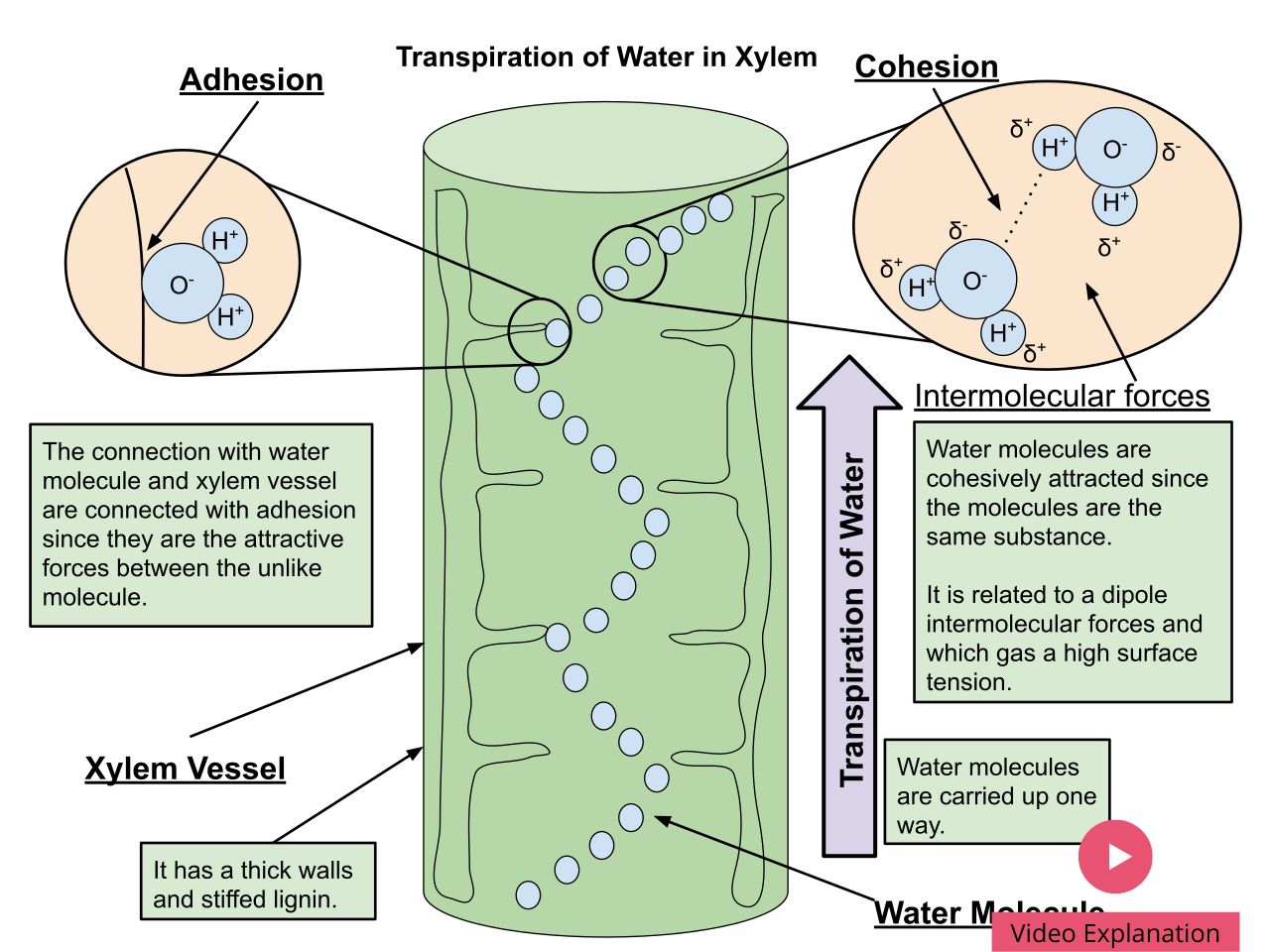
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The xylem, vessels and tracheids of the roots, stems and leaves are interconnected…
In earth science, erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth’s crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement.…
In botany, a stoma is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening.…
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. Mass flow of liquid water…
A cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of minute liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of…
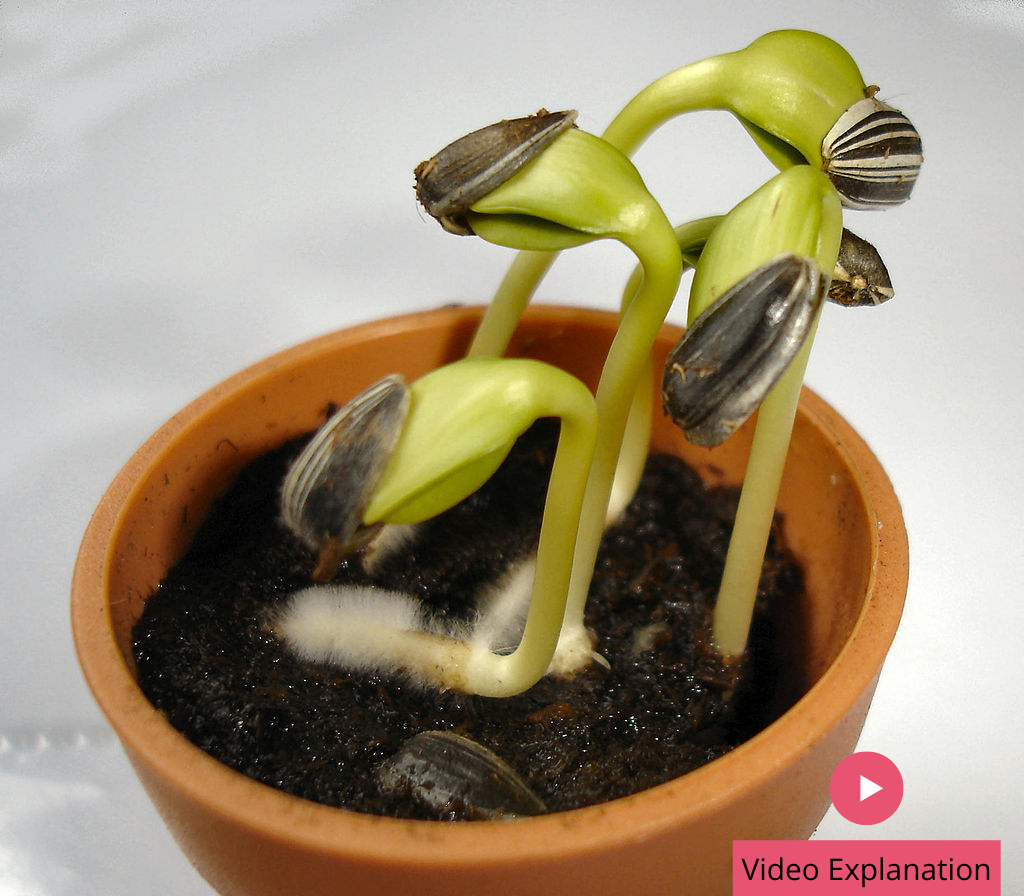
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ferns, bacteria, and the…
Climate Change, in the most simple terms, is a concept revolving around the long-term changes and alterations in weather temperatures and their overall patterns. The large-scale shifts in weather patterns, global warming, and the use of greenhouse gas emissions are some of the aspects of climate change itself. It is…
Even though both Weather and Climate are relatively similar and easy to understand, understanding the difference between the two is slightly complex. Before we dive into the blog’s main agenda, the question that arises is; why is it important to understand the difference between Climate and Weather? Global…
The Covid 19 pandemic has affected the whole world in one way or another, and 2020 without a doubt, has been a roller coaster ride! We have not only been forced to practice social distancing for months at end but, the pandemic has also affected all our routine decisions. Do…
While the phenomenon of identical twins may sound easy to comprehend, it is extremely important to understand what we mean by the term “Identical Twins” before diving deep into its features and other characteristics. Identical twins, also known as monozygotic, are twins that have been developed from a single egg/sperm.…
” If not thousands, there are hundreds of poisonous plants in the world, some of which can turn out to be deadly. “ Looking around, we see plants almost every day. While they may look harmless, they can contain some of the most deadliest poison known to mankind. Some of…
There are seven different learning styles. Most students fall across the spectrum of each of these styles. Some may be visual and spatial learners, while others are aural and musical learners. As there are various types of learners, it is not easy to stimulate learning for all students through just one learning…